Asalam 0 Alaikum dear friends, How are you? I hope you all are fine. friends in this post I am going to upload a post regard subject of Managerial Economics and topics will be covered are Advanced Demand Analysis, Demand Function and Total Average and Marginal Revenue.
Advanced Demand Analysis
DemandDemand Quantity of product that a consumer(group) is willing and able to purchase in a given time period at a given price level.
Demand = Desire + willingness + ability to purchase
Desire for a product.
Willing to pay for it.
Able to pay.
Demand analysis is to discover or determine the customer requests for a product in a particular market in specific time period considering all possible factors.
It helps Managers to forecasting future demand for a product.
It helps Managers to estimate future sale volume.
Ultimately it helps in decision making and price setting.
Law of Demand
Law of Demand states that quantity demanded will increase if price fall in given time period and vice versa.The law of demand describe the inverse relationship of price and quantity demanded keep other things constant.
Demand schedule a table showing the quantities of a good that a consumer is willing and able to buy at the prevailing price in a given time Demand function: is a function that describe how much of a commodity will be purchased at the prevailing prices of that commodity and related commodities, alternative income levels, and alternative values of other variables affecting demand.
Demand Function: It states the (functional/mathematical) relationship between the demand for the product ( dependent variable) and its determinants ( independent variables).
Qd X = f (Px , Pr , Y, T, Ey , Ep , Adv….)
Where,
Qd X = quantity demanded of good ‘X’
Px = the price of good X
Pr = the price of a related good(Substitutes/Complementary)
Y = income level of the consumer
T = taste and preference of the consumers
E y = expected Future income
E p = expected Future price
Adv = advertisement cost, etc.
Market Demand Curve
The market demand curve is the sum of the individual curves of all consumers in the market of a good.The market demand curve is graphically obtained by adding for the same price of all individual demand curves :
The market demand curve moves to the right as more consumers enter the market.
All variables affecting the individual demand curves also affect the market demand curve.
The Price of good, The Price of a related good, Income level of the Consumer, Taste and Preference of the Consumers, Expected Income, Expected Price, Advertisement costs… all are called determinants of demand.
The Demand Curve will shift(either forward or backward) by change in these determinants.
Determinants of Demand
Price of the goodPrice of related goods
Consumer’s Income
Taste, preference, fashions and habits
Population
Weather Condition
Advertisement and Salesmanship
Consumer’s future price expectation
Government policy (taxation)
Types of Demand
Direct and indirect demandDerived demand and autonomous demand
Durable and non durable goods demand:
Firm and industry demand
Total market and market segment demand
Short run and long run demand
Elasticity of Demand
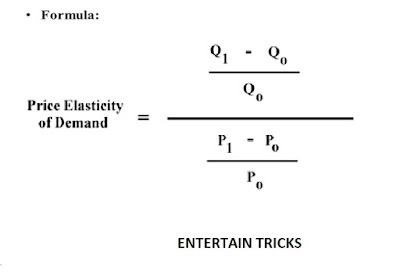
Elasticity of Demand: Demand elasticity refers to how sensitive the demand for a good is to changes in other economic variables, such as the prices and consumer income.Demand elasticity is calculated by taking the percent change in quantity of a good demanded and dividing it by a percent change in another economic variable.
The elasticity of demand may be as follows:
Price Elasticity
Income Elasticity and
Cross Elasticity
For example
Quantity demanded is 20 units at a price of Rs.500. When there is a fall in price to Rs. 400 it results in a rise in demand to 32 units.
%age change in demand = (32-20)/20 = 12/20
%age change in price = (500-400)/500 = 100/500
PED = (12/20)/(100/500) = 3
Quantity demanded is 20 units at a price of Rs.500. When there is a fall in price to Rs. 400 it results in a rise in demand to 32 units.
%age change in demand = (32-20)/20 = 12/20
%age change in price = (500-400)/500 = 100/500
PED = (12/20)/(100/500) = 3
The Determinants Of Price Elasticity Of Demand Nature of the commodity
Range of substitutes
Income level
Proportion of income spent on the commodity
Urgency of demand / postponement of purchase
Durability of a commodity
Purchase frequency of a product/ recurrence of demand
Time



Post a Comment